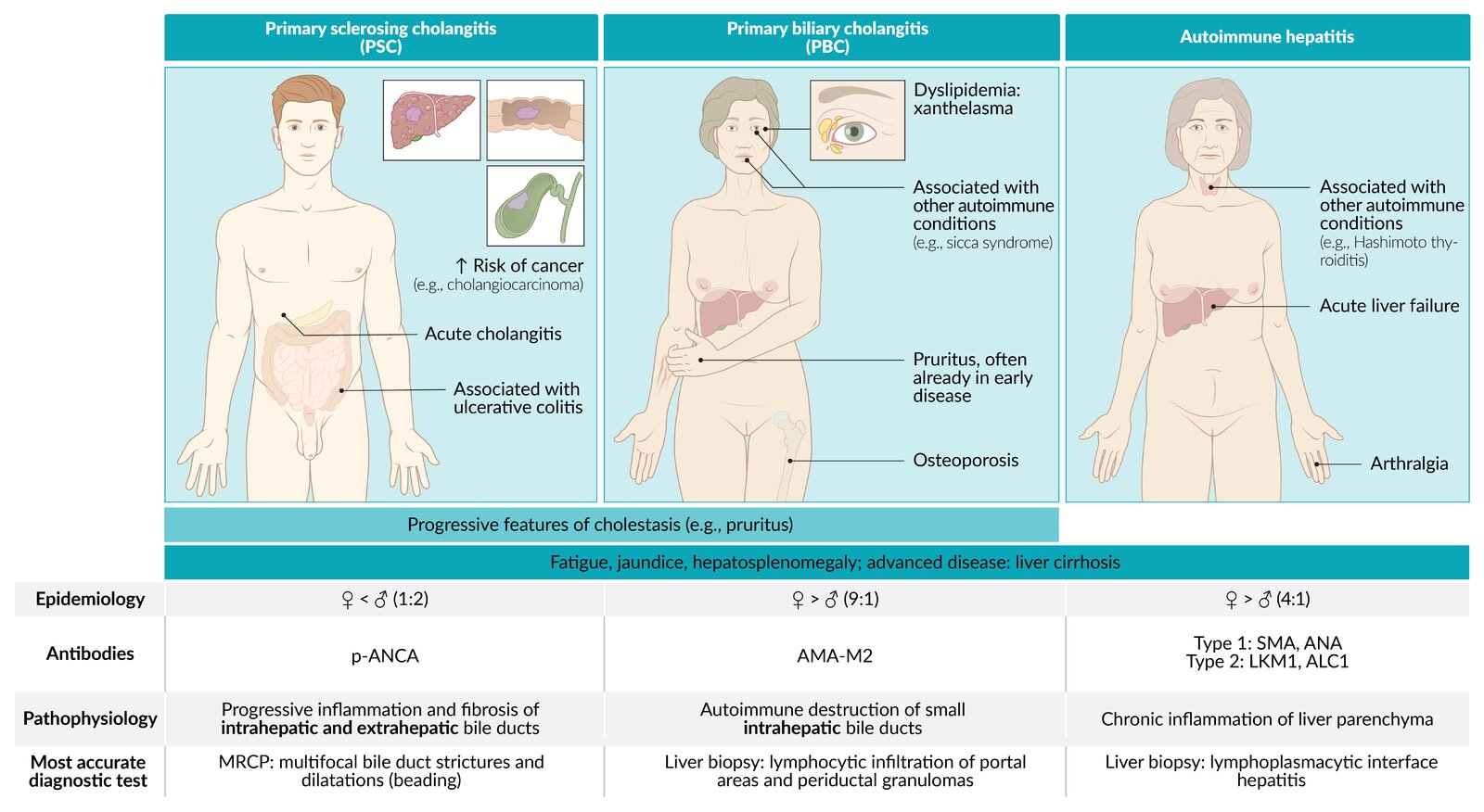
Primary biliary cholangitis
Etiology
- PBC is considered an autoimmune disease
- Often associated with other autoimmune conditions, e.g.:
- CREST syndrome
- Sicca syndrome
- Autoimmune thyroid disease, especially Hashimoto thyroiditis
- Celiac disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Pathophysiology
Inflammation and progressive destruction (likely due to an autoimmune reaction) of the small and medium-sized intrahepatic bile ducts (progressive ductopenia) → defective bile duct regeneration → chronic cholestasis → secondary hepatocyte damage due to increased concentration of toxins that typically get excreted via bile → gradual portal and periportal fibrotic changes → liver failure → liver cirrhosis and portal hypertension (in advanced stage)
Clinical features
Clinical features of PBC
Similar to PSC + xanthomas and xanthelasma
Patients with PBC are usually initially asymptomatic.
- Fatigue: most common and often the first symptom
- Marked pruritus: generalized
- Symptoms of cholestasis
- Jaundice
- Pale stool, dark urine
- Maldigestion (more common in advanced disease)
- Deficiency of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K)
- Signs of cirrhosis and portal hypertension
- Hepatomegaly with dull lower margin, RUQ discomfort
- Splenomegaly
- Hyperpigmentation
- Due to increased amounts of melanin; the exact cause and pathomechanism remain unclear.
- Xanthomas and xanthelasma
Diagnostics
Imaging (MRCP)
- PBC: normal
- PSC: stricturing of intra- and extra-hepatic bile ducts resembling beads on a string
- PSC = Stricture
- Liver chemistries: cholestatic pattern of injury
- ↑ ALP, ↑ GGT, ↑ direct bilirubin
- Mild transaminitis (or normal AST and ALT)
- Lipid panel: hypercholesterolemia
- PBC-specific autoantibodies
- Antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA) (present in > 95% of patients)
- Immunoglobulins (nonspecific)
- ↑ IgM
- Biopsy
- Because intrahepatic bile ducts are concentrated in the periportal regions, histopathology demonstrates periductal fibrosis predominantly in those regions.

- Because intrahepatic bile ducts are concentrated in the periportal regions, histopathology demonstrates periductal fibrosis predominantly in those regions.
Treatment
General principles
- Start pharmacotherapy with ursodeoxycholic acid for all patients.
- Offer supportive care, including management of cholestasis-associated pruritus.
- Liver transplantation is necessary if liver cirrhosis is advanced.
Pharmacotherapy
- First-line: ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA, ursodiol): a hydrophilic, nontoxic bile acid with immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, choleretic, and cytoprotective effects
- Slows disease progression and development of complications (e.g., esophageal varices)
- Prolongs transplant-free and overall survival
- Also used in primary sclerosing cholangitis, cholestasis of pregnancy, and small cholesterol stones